Table of Contents

Every sitting room is immaculate and comfortable. Very welcoming indeed is the all- time favourite couch waiting to bear your weight and tiredness whilst caressing you to relaxed levels of sleep and sheer joy of enjoying the world on your fingertips remotely. At office your seat is the get away from your boss and jibes from unwanted circles giving you the solace of focus at work and earning a sound bank balance. This sounds very good and we have successfully built our world on a couch or a seat. Prolonged sitting destroys the human anatomy slowly and unknowingly. We tend to ignore small muscle pains, back aches and bloating. We attribute all this to eating disorders. Dissect your daily routine and you will find that in a day of of work and 8 hours of sleep, you are glued to your chair at home or office in a sitting position for almost 11 to 13 hours a day. Sitting for long hours is actually associated to sedentary behaviour and minimum muscle movement. So stop assigning your ailments to eating disorders and seriously consider changing your habit of routine sitting at work or before the TV for prolonged hours. Kick the couch and kick start your day with brisk movements of simple exercises of climbing the stairs, walking to your nearest grocery store, fetching your own cup of coffee at office, take a break to work out the gym in your office, stand up from your seat at regular intervals and work and walk around when you need to attend to a phone call. The bottom line is to avoid the couch or chair when you may well exercise your muscles whenever possible. Do not put off exercising your muscles and ignore the necessity of slight movements, for otherwise it leads to risk of serious health consequences.
1. Heart Attacks
Long hours of sitting do not encourage blood flow or circulation. Fatty acids clog the heart and increase the risk of heart attacks. Although a sedentary position is one of the causes to poor heart health, the risk associated is high. It is advised to reduce your sitting hours and take short breaks for every half hour of sitting. A proper heart function is dependent on the pumping of blood and if there is more of fatty acids and less of blood present, then your heart calls for a change in habits such as setting a reminder to take a short break. Studies have shown that regular gym and exercise regime to compensate for the long hours of sitting do not really reduce the risk of heart attacks. It is best to relieve the clogging of fatty acids with frequent short breaks if sitting for long hours continuously between 2 to 10 hours at a stretch. [1]

2. Cancer
Although there is no established link to cancer and sitting for long hours, yet the risk of cancer occurring is very high due to sitting for long hours. Medical research and studies have linked the risk of endometrial cancer or uterine cancer occurring in women and colon cancer both, in men and women who sat for long hours to be very high as compared to those who sat fixed for lesser hours. The risk was higher in case of women who watched TV consistently. Cutting down on sedentary time is highly recommended since natural antioxidants produced are very low in a state of inactivity. [2]

3. Edema
Pooling of fluids in our legs is at a high risk when we sit at our desk or on the couch for long hours. The blood circulation slows down resulting in formation of fluid pools or edema. This also leads to varicose veins. Muscle contractions are necessary to improve blood circulation and reduce cholesterol levels.
4. Obesity
Low appetite and digestion capacity also leads to low metabolism. This leads to obesity which in turn is the root cause of many heart related diseases. Unintentional movement throughout the day helps in weight control and this is to be adopted by all to avoid weight gain and obesity thereon. Truck drivers and those employed at an office are largely exposed to the risk of obesity if they do not venture for short strolls or leg and body movements.
5. Diabetes
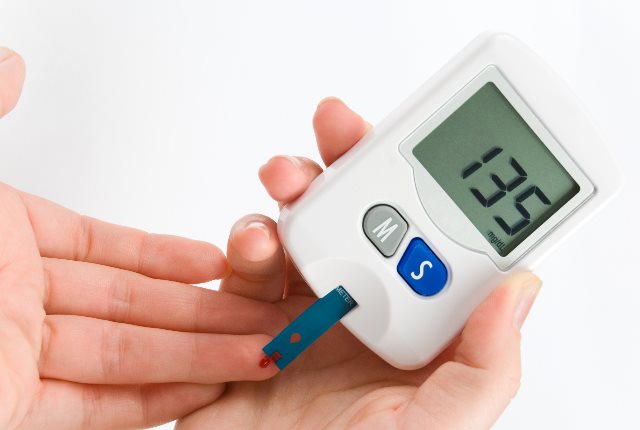
The risk of diabetes Type 2 is very high in a sedentary position. The pancreas produces insulin- a hormone that carries glucose to cells for energy. When the cells do not absorb the insulin and convert the same to energy, the pancreas produce insulin in excess leading to diabetes. Short breaks of walking around and using the stairs instead of lifts and elevators are recommended to break the monotony of being seated for too long. [5]
6. Increased Waist Line
The dangers of a huge waist are nonetheless associated with long hours of sitting. Even people who exercise regularly but have to be seated in a fixed position for long hours, are prone to having a large waist line. Inflammation sets in the form of higher levels of C- reactive protein and blood fats or triglycerides. Research reveals that in men with waist line above 40 inches and women above 35 inches the risk of increase in waist line is higher, when they sit for prolonged hours. However, those seated for a prolonged time but take frequent short walking trips, sport a small waist line reducing the accumulation of C-Reactive protein and triglycerides. [6]

7. Spine Curvature Disorder
The vertebrae or spine is made up of small bones stacked one on top of the other. The spine has gentle curves to it when viewed from the side. The curvature is to absorb the stress and gravity of our body movement. These small bones or discs get squashed when we sit for prolonged hours. Movement is the best anecdote to avoid this disorder. When we move around, the blood circulation between these bones are encouraged with an assured supply of nutrients to the bones. The spine remains strong. [7]

8. Abdomen Weakening
Abdominal muscles help to keep us upright when we stand or sit. They define the postural support. The transverse abdominus muscle is the deepest muscle that has a direct impact upon the body posture. It supports the spine in its forward posture and external obliques support the spine when upright. Sitting, bending forward, backward, walking is all wholesomely dependent on the spine which in turn draws its functional support from the abdominal muscles. The abdominal muscle use diminishes when we slump in our couch or chair. Sitting for prolonged hours leads to a tight abdomen restricting movements of bending in any direction which is not so good news for the abdomen.
9. Enhances Slow Thinking
Brain functioning slows down when seated for a prolonged time. Movement of muscles propels blood circulation and the heart too pumps the required quantity of blood which in turn supplies the required quantity of nutrients to the brain. The brain is alert when muscle movement sets blood circulation. Prolonged sitting leads to dull thinking.
10. Pulmonary Embolism
The risk of blood clot in the lungs is high due to prolonged sitting. This condition is also called pulmonary embolism. The blood clot in the lungs is due to the blood carrying a substance from any part of the body to the lungs. This is more often from the veins in the legs. Supply of fresh oxygen and blood are essential for strong lungs. In order to free the clots from the legs, movements of the legs are highly recommended along with seating posture changes.[10]